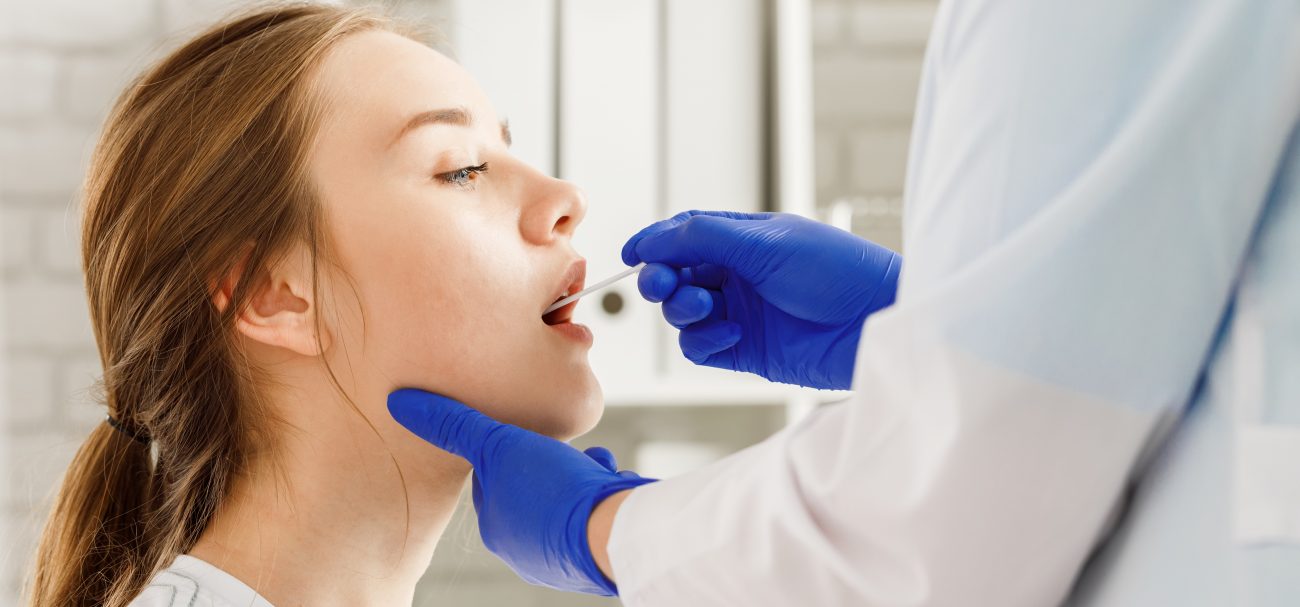
Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)
AMR occurs when bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites change over time and no longer respond to medicines, making infections harder to treat, increasing the risk of disease spread, severe illness and death. The emerging increase of microbes that are resistant to antimicrobial treatments has become a global public health concern that threatens the effective treatment of infectious diseases:
PGEU Position Paper on Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)
Executive Summary:
Community pharmacists play a key role in infection prevention and promoting antimicrobial stewardship through a range of professional services including:
PGEU adopted the PGEU Position Paper on Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR), with a set of recommendations for policy makers at national and European level to take urgent action to address this silent pandemic, as well as highlights the European community pharmacists’ role in tackling AMR, and further providing examples of PGEU members’ contribution to curbing this health threat.
Key messages are available here.

PGEU Best Practice Paper on Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)
Pharmacists intervention in this area includes not only the best dispensing practices, but also information about the importance of taking the antibiotic as prescribed, monitoring and informing patients about possible side effects, adverse reactions and drug interactions. PGEU supports European Antibiotic Awareness Day.
The emerging and steady increase of microbes that are resistant to antimicrobial treatments has become a global public health concern that threatens the effective treatment of infectious diseases. In the EU alone, it is estimated that 33,000 people die each year due to infections caused by resistant bacteria.
Community pharmacists are often the first and final contact in the health system before a pharmaceutical, a device or another health intervention is supplied. They play pivotal roles in counselling patients and promoting antimicrobial stewardship. They provide preventative action, referral, disposal, treatment in the pharmacy and constantly strive for quality improvements and innovation in pharmacy practice.
Because the use of antibiotics in both human and veterinary medicine is associated with the emergence of resistance, it is crucial that antibiotics are prescribed and dispensed responsibly and used correctly. Non-adherence to antibiotic therapies may result in antibiotic resistance, as suboptimal doses of antibiotic therapy can result in insufficient antibiotic exposure for eradicating infectious bacteria and potentially create an environment that promotes antibiotic resistance. Therefore understanding the correct use of antibiotics and the reasons behind poor adherence to antibiotic therapies (e.g. regimens having several daily doses), is crucial if the developing phenomenon of antibiotic resistance is to be controlled.
Pharmacists intervention in this area includes not only the best dispensing practices, but also information about the importance of taking the antibiotic as prescribed, both in terms of regimen (e.g. every 12h) and extension of treatment (e.g. for 7 days).
Furthermore, by monitoring and informing patients about possible side effects, adverse reactions and drug interactions, pharmacists contribute to the correct use of antibiotics and identify possible causes for non-adherence.

European Antibiotics Awareness Day
Since its inception in 2008, PGEU has systematically supported and engaged in the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control’s (ECDC) European Antibiotic Awareness Day (EAAD) to promote the prudent use of antibiotics. In recent years this has been further enhanced by the use of social media to raise awareness of the issue of AMR and to encourage the prudent use of antibiotics.
In 2013-2014 the PGEU actively contributed to the ECDC’s consultation on the development of a toolkit for self-medication of antibiotics in collaboration with the Standing Committee of European Doctors (CPME). This resulted in a suite of materials available in all EU languages which can be adapted as necessary to raise awareness of the dangers of self-medication with antibiotics and their ineffectiveness against colds and seasonal influenza (‘flu).
PGEU also provided significant input into the ECDC’s EU guidelines on the prudent use of antimicrobials in humans which specifically mentions the role of pharmacists in ensuring the prudent use of antimicrobials.
WHO Europe
In 2014, PGEU collaborated with WHO Europe to survey community pharmacists, other healthcare professionals, government institutions and health service providers to outline the role community pharmacists can play in tackling AMR and encouraging the prudent use of antimicrobials. This collaboration resulted in a report which identifies community pharmacists as important allies in the fight against AMR and that pharmacists already have experience in treating their patients with antibiotics, both responsibly and within the appropriate legal framework.
Additionally, the report concludes that pharmacists are among the best positioned healthcare professionals to facilitate the appropriate use of antibiotics and, therefore, have an essential role to play in tackling AMR alongside policy-makers and general practitioners. PGEU also engages in WHO’s World Antibiotics Awareness Week (WAAW) campaign which complements the ECDC’s EAAD.
Multi-stakeholder Collaboration
PGEU is one of the founding partners of the pan-European interdisciplinary stakeholder collaboration “medsdisposal”. #medsdisposal is a campaign to raise awareness on the appropriate disposal of expired or unused medicines in Europe and includes associations representing European healthcare, industry and student organisations. Crucial to this project’s relevance is an interactive map of Europe with direct links to the official websites providing information on the appropriate way of disposing medicines in each country in the national language(s).
In order to increase awareness of this website, social media is used extensively to guide members of the public to the resources on the campaign’s website:
• https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCAX8cA8IfIwk7iH4DtB5FZg/videos
• https://www.facebook.com/medsdisposaleu-890282831045021/
• https://twitter.com/hashtag/medsdisposal
- In 2019: estimated 4.95 million deaths (1.27 million deaths directly attributable to resistance to medicines).
- Every year 35,000 EU/EEA citizens die from infections with antibiotic resistant bacteria, with an annual cost of over €1.5 billion to EU health systems.
- By 2050: 10 million lives/year + 100 trillion US dollars of economic output are at risk.
PGEU Position Paper on Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)
Executive Summary:
- Community pharmacists play a key role in antimicrobial stewardship, including counselling and advising on the prudent use of antibiotics and other antimicrobials, as well as their correct disposal.
- The revision of the General Pharmaceutical Legislation offers an opportunity to reinforce stewardship programs for antimicrobials.
- Pharmacies can be used as healthcare settings for effective public health campaigns on Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR).
- Pharmacists are healthcare professionals qualified to perform point of care testing to screen for early signs of infectious diseases and differentiate between viral and bacterial infections.
- Community pharmacists have shown that the network of pharmacies spread across the territory offers highly accessible testing services to the population during the COVID-19 pandemic (in at least 12 countries).
- Community pharmacists play a fundamental role in pharmacy-based vaccination which is a valuable tool in the fight against AMR.
- Integrated clinical pathways available in some countries have shown positive results in protocol-based dispensing of antimicrobials following a test done at the pharmacy.
- Community pharmacists’ access to electronic health records can be used to increase the early warning systems regarding monitoring shortages of antimicrobials.
Community pharmacists play a key role in infection prevention and promoting antimicrobial stewardship through a range of professional services including:
- Providing patients with high quality information on the appropriate use of antimicrobials to ensure adherence to treatment.
- Raising awareness about the correct disposal of antimicrobials.
- Having in place pharmacy-led disposal and collection schemes.
- Offering pharmacy-based vaccination programs. Vaccines can contribute to reduce the overall reliance on antimicrobials by preventing infectious diseases.
- Performing rapid diagnostic tests to detect bacterial infection and minimize the use of antimicrobials only when they are really needed (e.g. France, Italy, Ireland).
PGEU adopted the PGEU Position Paper on Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR), with a set of recommendations for policy makers at national and European level to take urgent action to address this silent pandemic, as well as highlights the European community pharmacists’ role in tackling AMR, and further providing examples of PGEU members’ contribution to curbing this health threat.
Key messages are available here.

PGEU Best Practice Paper on Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)
Pharmacists intervention in this area includes not only the best dispensing practices, but also information about the importance of taking the antibiotic as prescribed, monitoring and informing patients about possible side effects, adverse reactions and drug interactions. PGEU supports European Antibiotic Awareness Day.
The emerging and steady increase of microbes that are resistant to antimicrobial treatments has become a global public health concern that threatens the effective treatment of infectious diseases. In the EU alone, it is estimated that 33,000 people die each year due to infections caused by resistant bacteria.
Community pharmacists are often the first and final contact in the health system before a pharmaceutical, a device or another health intervention is supplied. They play pivotal roles in counselling patients and promoting antimicrobial stewardship. They provide preventative action, referral, disposal, treatment in the pharmacy and constantly strive for quality improvements and innovation in pharmacy practice.
Because the use of antibiotics in both human and veterinary medicine is associated with the emergence of resistance, it is crucial that antibiotics are prescribed and dispensed responsibly and used correctly. Non-adherence to antibiotic therapies may result in antibiotic resistance, as suboptimal doses of antibiotic therapy can result in insufficient antibiotic exposure for eradicating infectious bacteria and potentially create an environment that promotes antibiotic resistance. Therefore understanding the correct use of antibiotics and the reasons behind poor adherence to antibiotic therapies (e.g. regimens having several daily doses), is crucial if the developing phenomenon of antibiotic resistance is to be controlled.
Pharmacists intervention in this area includes not only the best dispensing practices, but also information about the importance of taking the antibiotic as prescribed, both in terms of regimen (e.g. every 12h) and extension of treatment (e.g. for 7 days).
Furthermore, by monitoring and informing patients about possible side effects, adverse reactions and drug interactions, pharmacists contribute to the correct use of antibiotics and identify possible causes for non-adherence.

European Antibiotics Awareness Day
Since its inception in 2008, PGEU has systematically supported and engaged in the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control’s (ECDC) European Antibiotic Awareness Day (EAAD) to promote the prudent use of antibiotics. In recent years this has been further enhanced by the use of social media to raise awareness of the issue of AMR and to encourage the prudent use of antibiotics.
In 2013-2014 the PGEU actively contributed to the ECDC’s consultation on the development of a toolkit for self-medication of antibiotics in collaboration with the Standing Committee of European Doctors (CPME). This resulted in a suite of materials available in all EU languages which can be adapted as necessary to raise awareness of the dangers of self-medication with antibiotics and their ineffectiveness against colds and seasonal influenza (‘flu).
PGEU also provided significant input into the ECDC’s EU guidelines on the prudent use of antimicrobials in humans which specifically mentions the role of pharmacists in ensuring the prudent use of antimicrobials.
WHO Europe
In 2014, PGEU collaborated with WHO Europe to survey community pharmacists, other healthcare professionals, government institutions and health service providers to outline the role community pharmacists can play in tackling AMR and encouraging the prudent use of antimicrobials. This collaboration resulted in a report which identifies community pharmacists as important allies in the fight against AMR and that pharmacists already have experience in treating their patients with antibiotics, both responsibly and within the appropriate legal framework.
Additionally, the report concludes that pharmacists are among the best positioned healthcare professionals to facilitate the appropriate use of antibiotics and, therefore, have an essential role to play in tackling AMR alongside policy-makers and general practitioners. PGEU also engages in WHO’s World Antibiotics Awareness Week (WAAW) campaign which complements the ECDC’s EAAD.
Multi-stakeholder Collaboration
PGEU is one of the founding partners of the pan-European interdisciplinary stakeholder collaboration “medsdisposal”. #medsdisposal is a campaign to raise awareness on the appropriate disposal of expired or unused medicines in Europe and includes associations representing European healthcare, industry and student organisations. Crucial to this project’s relevance is an interactive map of Europe with direct links to the official websites providing information on the appropriate way of disposing medicines in each country in the national language(s).
In order to increase awareness of this website, social media is used extensively to guide members of the public to the resources on the campaign’s website:
• https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCAX8cA8IfIwk7iH4DtB5FZg/videos
• https://www.facebook.com/medsdisposaleu-890282831045021/
• https://twitter.com/hashtag/medsdisposal
Downloads
PGEU Positon Paper on Antimicrobial Resistance
PGEU key messages on Antimicrobial Resistance
PGEU Best Practice Paper on AMR 2020
PGEU Community Pharmacy analysis ECDC Survey on Healthcare Workers' Knowledge, Attitudes and Behaviours on Antibiotics, Antibiotic Use and Antibiotic Resistance in the EUEAA
PGEU Response to EC Consultation on EC AMR Action Plan
All Policies